Author: J Kishore Kumar (@justjkk)
Abstract
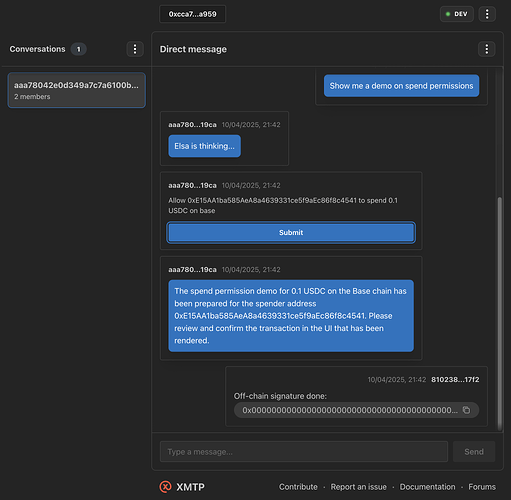
This content type provides a standard format for triggering on-chain calls typically by a programmatic agent like an AI agent responding to a user request. The client handling the content type SHOULD provide the user with an option to execute the provided transaction data and MAY track the status of the transaction by publishing another message with the transaction reference content type (XIP-21).
Motivation
The goal of the wallet send calls content type is to provide a rich interaction between an AI agent and the user and allow for on-chain actions like sending, swapping, lending tokens and any other DeFi protocol that can be represented as a single or a sequence of on-chain transactions. As XMTP natively represents users by their wallet address, implementing this content type benefits the ecosystem for both the current DeFAI use-case as well as any future use-case that enables on-chain interaction like minting NFT or registering votes on a group for a DAO proposal, etc.
Specification
Content type
{
authorityId: "xmtp.org",
typeId: "walletSendCalls",
versionMajor: 1,
versionMinor: 0,
}
Wallet send calls schema
type WalletSendCallsParams = {
version: string;
chainId: `0x${string}`; // Hex chain id
from: `0x${string}`;
calls: {
to?: `0x${string}` | undefined;
data?: `0x${string}` | undefined;
value?: `0x${string}` | undefined; // Hex value
gas?: `0x${string}` | undefined;
metadata?: {
description: string;
transactionType: string;
} & Record<string, any>;
}[];
capabilities?: Record<string, any> | undefined;
};
Rationale
Aligning this XIP with the existing EIP-5792 specification simplifies the client integration and by default enables features like Paymaster and Bundling(if using ERC-4337 smart wallet) by negotiating the wallet capabilities. For an EOA wallet that does not support the EIP-5792 Wallet API, the client SHOULD fallback to triggering the eth_sendTransaction API one or more times depending on the call data.
Backward compatibility
To maintain backward compatibility, a content fallback is stored in the codec as text — ensuring that the intent of the wallet-send-calls content type is conveyed even in non-supporting clients.
Test cases
Test cases will validate the interpretation of schema type and effective use of a content fallback. These are essential for ensuring interoperability across XMTP platforms.
Reference implementation
You can find a WIP reference implementation of this wallet-send-calls content type in HeyElsa/xmtp-js repo fork under the content-types/content-type-wallet-send-calls directory.
Security considerations
The following security risks are identified and clients implementing this content type should take necessary precautions.
Threat model
Content injection
The content type defines parameters that will end up as arguments to functions and since this content type may be coming from an untrustworthy user or agent, care should be taken to sanitize the input before using the parameters in any code. Typescript may provide only an indication about the parameter constraints and does not provide runtime validation. Even if runtime validation is supported, the client implementation still SHOULD sanitize the input based on the context of where the parameter may end up in. Eg: SQL injection, XSS.
Spoofing
The user visible part of the transaction is typically the description part of the metadata which could be completely different from the actual transaction data if coming from a malicious agent. So, the user may end up performing The client SHOULD mitigate this by doing one or more of the following:
- Maintain an allowlist of users or agents whose messages it trusts.
- Perform transaction simulation and cross-check it against the metadata or override the metadata that is displayed to the user.
- Display a warning or disclaimer alerting the user that the metadata description may not be trustworthy and to use their judgement.
Informed consent
Because the data could be coming from a confused/malicious agent, the client implementation MUST NOT automatically sign or execute the transaction. The user should always provide their confirmation after reviewing either the metadata or the simulation results. This also protects against any possible confusion or hallucination by the AI agent.
Privacy considerations
The client implementation SHOULD take care not to accidentally expose the IP address of the user to the agent indirectly. Eg: Passing the paymaster URL that is provided by the agent to the wallet may expose the user’s IP if the wallet queries the paymaster API from the user’s device.
Copyright
Copyright and related rights waived via CC0.